| dc.contributor.author | Lone, Astrid | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2011-10-21T08:09:00Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2011-10-21T08:09:00Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2011 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/11250/182480 | |
| dc.description | Master's thesis in Environmental technology | en_US |
| dc.description.abstract | Low dosage hydrate inhibitors (LDHIs) is a cost-effective alternative to traditional thermodynamic inhibitors (THIs), like methanol and glycols, to prevent the occurrence of natural gas hydrates in gas and oilfield operations. One class of LDHIs is the kinetic hydrate inhibitors (KHIs). KHIs have been used commercially in the field for the last 15 years, and the development and search for new KHIs is an ongoing process.
This report describes how high pressure rocker rigs can be used to rank KHIs based on their effectiveness and efficiency under different conditions.
The high pressure rocker rig used for this thesis was delivered at the end of November, and
the experiments started on December 1st. The last experiment took place May 2nd. The
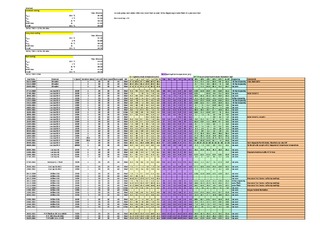
Rocking Cell RC5 has five cells that provide five individual results from every experiment. This makes it a very time-effective rocker rig compared to, say, autoclaves, where one normally only obtains one result per day. Since the start-up with the rocker rig in December there have been no major problems, and so it has been a very reliable piece of equipment.
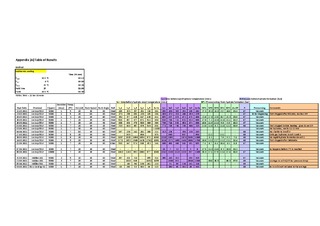
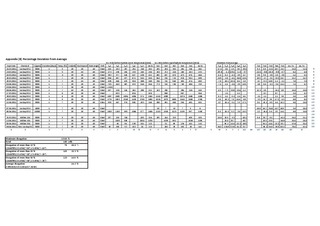
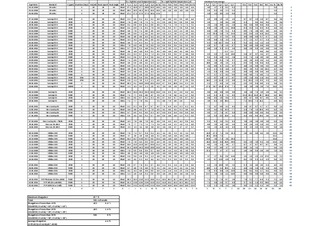
A procedure for the Rocking Cell RC5 has been established. Experiments are run using a constant cooling method and an isothermal method. The reproducibility was found to be best using the constant cooling method. Compared to alternative apparatus the reproducibility has proven to be very good. Reported information from experiences using autoclaves, say that the scattering in hold time using non-precursor methods is usually 30-40% on either side of average of series. Using the constant cooling method the scattering in hold time is found to be within 4.4%.
The main focus of these thesis has been testing four already known KHIs; Luvicap 55W, Luvicap EG, Inhibex 101 and Inhibex 501. The chemicals are ranked based on how well they inhibit the gas hydrate formation. Inhibex 101 was found to be the best one, both using the constant cooling method and the isothermal method.
Since there are no thorough published studies available on the use of rocker rigs to rank the performance of KHIs, the results cannot be compared to experiments from other groups. For some results, more tests should therefore be run to check the validity of the results. | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | eng | en_US |
| dc.publisher | University of Stavanger, Norway | en_US |
| dc.relation.ispartofseries | Masteroppgave/UIS-TN-IMN/2011; | |
| dc.subject | gas hydrates | en_US |
| dc.subject | kinetic hydrate inhibitors | en_US |
| dc.subject | teknisk miljøvern | en_US |
| dc.subject | offshore teknologi | en_US |
| dc.title | Establishing a new high pressure steel multi-cell rocker rig for kinetic hydrate inhibitor testing | en_US |
| dc.type | Master thesis | en_US |
| dc.subject.nsi | VDP::Mathematics and natural science: 400 | en_US |